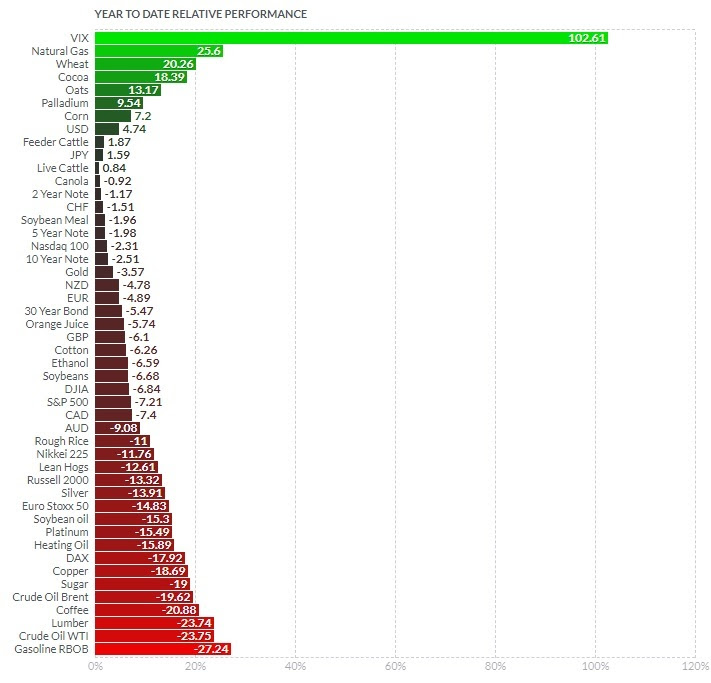
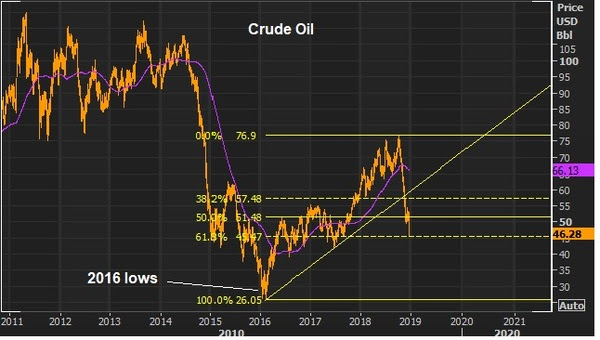
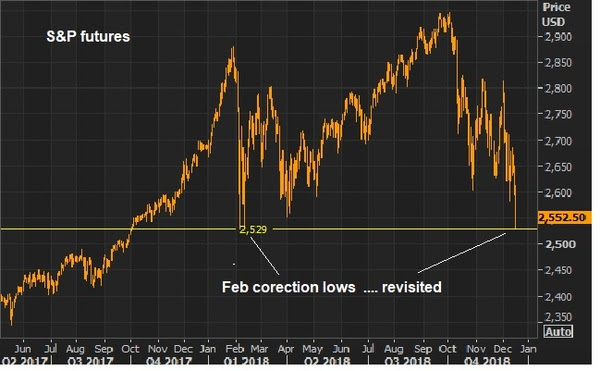
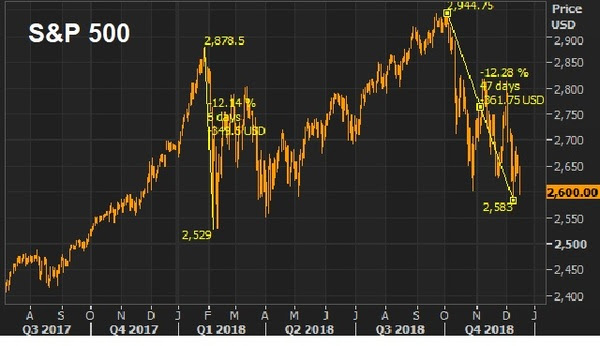
January 3, 5:00 pm EST
As we’ve discussed, the dysfunctional stock market has put pressure on Trump to stand down and make a deal with China.
And Apple’s CEO, Tim Cook, turned up that pressure yesterday. In a letter to investors, he warned that Apple, the biggest and most powerful company in the world, would have lower revenue in the quarter that just ended. The blame was placed on economic deceleration in China —due to the trade dispute.
Now, it’s clear that Cook wanted to draw attention to the impact of the trade dispute. And the media was happy to run with that story today.
But the slowdown at Apple last quarter also had a lot to do with “fewer iPhone upgrades than anticipated.” This was tossed into the context of slower economic activity in China, which makes it look like a macro issue. But Apple also has a micro issue. They seem to have exhausted the compelling innovation that has historically gotten iPhone users excited about buying the latest and greatest phone. The older models are still pretty great. No reason to upgrade.
So, Apple has used a violent market and slowdown in China, perhaps, in an attempt to divert attention away from the slowing device business.
The good news: Even if they don’t develop the next world-changing device, they have a services business (Apple pay, Apple Music, iCloud Drive, AppleCare and the iTunes App store) that is producing almost as much revenue as Facebook.
And the stock is incredibly cheap. On trailing twelve months, the stock trades at 12 times earnings. But if we back out the nearly $240 billion of cash Apple is sitting on, the business at Apple is being valued at $437 billion. That’s about 7 times trailing twelve month earnings.